Cross-Region Replication
TigerGraph’s Cross-Region Replication (CRR) feature allows users to keep two or more TigerGraph clusters in different data centers or regions in sync. One cluster is the primary cluster, where users perform all normal database operations, while the other is a read-only Disaster Recovery (DR) cluster that syncs with the primary cluster. CRR includes complete native support for syncing all data and metadata including automated schema, user, and query changes.
Use cases
For users of TigerGraph, cross-region replication helps deliver on the following business goals:
-
Disaster recovery: A dedicated remote cluster in another region allows you to retain your data in the event of a disaster.
-
Enhanced availability: Enhance inter-cluster data availability by synchronizing data using Read Replicas across two clusters
-
Enhanced performance: If your application is spread over different regions, you can take advantage of data locality to avoid network latency through CRR.
-
Improved system load balancing: CRR allows you to distribute computation load evenly across two clusters if the same data sets are accessed in both clusters.
-
Data residency compliance: CRR allows you to replicate data between different data centers or regions to satisfy compliance requirements. Additionally, you can set up clusters in the same region to satisfy more stringent data sovereignty or localization business requirements.
-
Blue/green deployment: CRR allows you to set up the clusters as part of Blue/Green deployment purposes for agile upgrades.
What is included
The following information is automatically synced from the primary cluster to the DR cluster:
-
All data in every graph
-
All graph schemas, including tag-based graphs
-
All schema change jobs
-
All users and roles
-
All queries in every graph. Queries that are installed in the primary cluster are automatically installed in the DR cluster.
Exclusions
The following information and commands are not synced to the DR cluster:
-
GraphStudio metadata
-
This includes graph layout data and user icons for GraphStudio.
-
-
Loading jobs
-
This refers to the loading job definitions only. Data loaded through a loading job is still replicated from the primary to the DR cluster.
-
-
gadminconfigurations (e.g.gadmin config set GSQL.BasicConfig.LogConfig.LogLevel DEBUG)
The following commands/actions and will stop syncing to the DR cluster:
-
gbar restorewhile the cross-region replication is enabled. -
gsql --resetcommand -
The following GSQL commands:
-
EXPORTandIMPORTcommands -
DROP ALLandCLEAR GRAPH STORE
-
|
When the primary cluster executes an See Sync an outdated cluster on how to bring an outdated DR cluster back in sync. |
CRR logic
The following diagram is a simplified illustration of the key components and logic behind CRR:
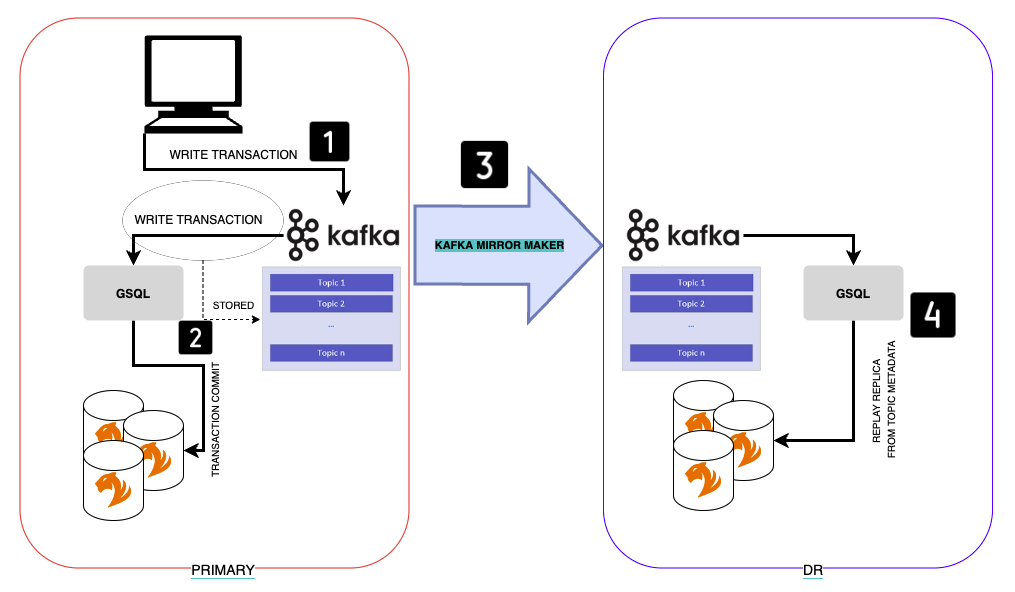
CRR logic is divided into two layers:
-
Infrastructure layer: Kafka Topic replication via Kafka MirrorMaker from primary Kafka to DR Kafka.
-
GSQL layer: GSQL replaying replicas on DR from Kafka topic.
|
A "replica" in Kafka topic context is the committed operation of a write transaction ( Kafka MirrorMaker is a stand-alone tool (out-of-the-box from TigerGraph) for copying data between two Kafka, in this specific case between primary Kafka and DR Kafka. |
This following is the flow of replication done by Cross-region replication feature. Each step correspond to the numbered steps in the previous diagram:
-
Application sends a write transaction to the primary (e.g.
CREATE VERTEX PERSON). -
This transaction is committed successfully and stored in Kafka Metadata.
-
Kafka MirrorMaker replicates the Metadata from primary Kafka to DR kafka maintaining the same unique identification.
-
GSQL on DR replays this replica from DR Kafka metadata and commits the change.
FAQ
See the FAQ for frequently asked questions about CRR.