Minimum Spanning Tree
Given an undirected and connected graph, a minimum spanning tree is a set of edges that can connect all the vertices in the graph with the minimal sum of edge weights. The library implements a parallel version of Prim’s algorithm:
-
Start with a set A = { a single vertex seed }
-
For all vertices in A, select a vertex y such that
-
y is not in A, and
-
There is an edge from y to a vertex x in A, and
-
The weight of the edge e(x,y) is the smallest among all eligible pairs (x,y).
-
-
Add y to A, and add the edge (x,y) to MST.
-
Repeat steps 2 and 3 until A has all vertices in the graph.
If the user specifies a source vertex, this will be used as the seed. Otherwise, the algorithm will select a random seed vertex.
Notes
If the graph contains multiple components (i.e., some vertices are disconnected from the rest of the graph), then the algorithm will span only the component of the seed vertex.
If you do not have a preferred vertex, and the graph might have more than one component, then you should use the Minimum Spanning Forest algorithm instead.
Specifications
tg_mst (VERTEX opt_source, SET<STRING> v_type_set, SET<STRING> e_type_set,
STRIN weight_attribute, STRING weight_type, INT maximum_iteration = -1,
BOOL print_results = TRUE, STRING result_attribute = "", STRING file_path = "")Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
|
The vertex to use as a source (optional). Provide the vertex ID and type as a tuple: |
N/A |
|
Names of vertex types to use |
(empty set of strings) |
|
Names of edge types to use |
(empty set of strings) |
|
Name of edge weight attribute |
(empty string) |
|
Data type of edge weight attribute (must be |
(empty string) |
|
Maximum number of edges to include. If less than the number of vertices minus 1, then the result is not a true spanning tree. |
-1 |
|
If True, output JSON to standard output |
True |
|
If not empty, store result values ( |
(empty string) |
|
If not empty, write output to this file. |
(empty string) |
Example
In the graph social10, we consider only the undirected Coworker edges.
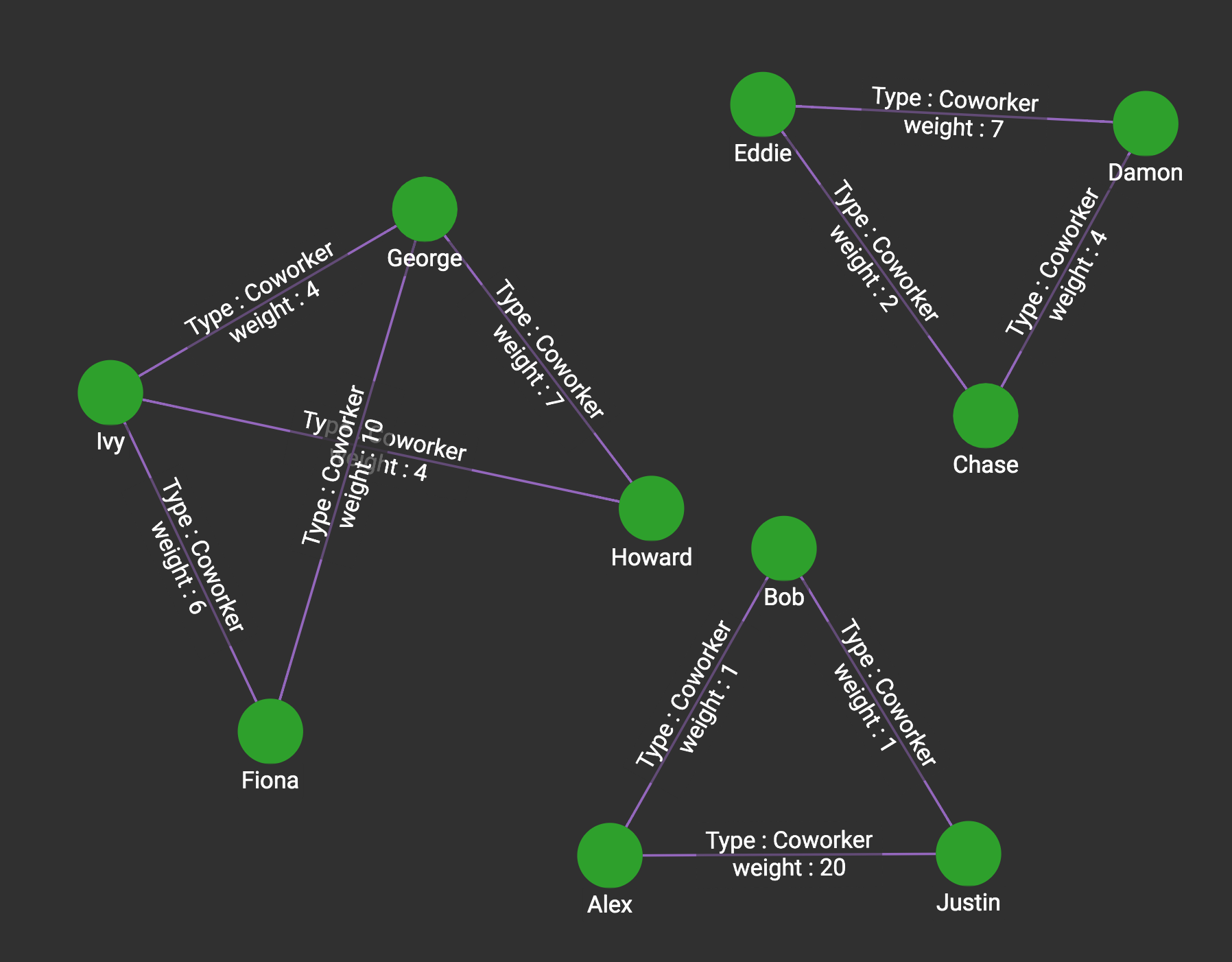
This graph has 3 components. Minimum Spanning Tree finds a tree for one component, so which component it will work on depends on what vertex we give as the starting point.
If we select Fiona, George, Howard, or Ivy as the start vertex, then it works on the 4-vertex component on the left. You can start from any vertex in the component and get the same or an equivalent MST result.
The figure below shows the result of
# Use _ for default values
RUN QUERY mst(("Ivy", "Person"), ["Person"], ["Coworker"] "weight", "INT",
_, _, _, _)Note that the value for the one vertex is ("Ivy", "Person"). In GSQL, this 2-tuple format which explicitly gives the vertex type is used when the query is written to accept a vertex of any type.
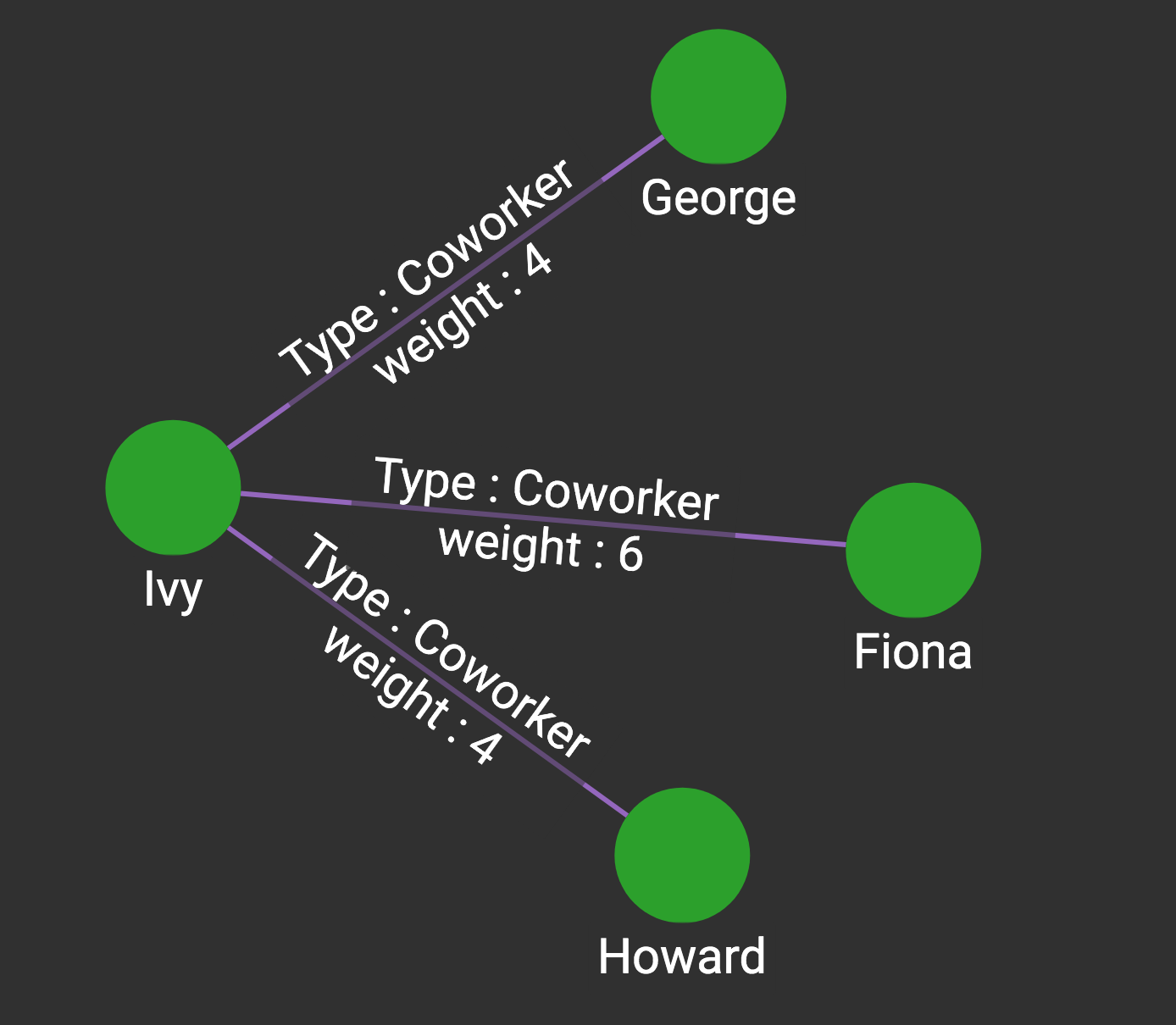
File output:
From,To,Weight
Ivy,Fiona,6
Ivy,Howard,4
Ivy,George,4The attribute version requires a boolean attribute on the edge, and it will assign the attribute to "true" if that edge is selected in the MST: