Installation Guide
This guide describes how to install the TigerGraph platform either as a single node or as a multi-node cluster, interactively or non-interactively.
| If you signed up for the Enterprise Free license, you also have access to the TigerGraph platform as a Docker image or a virtual machine (VirtualBox) image. Follow the instructions in Get Started with Docker to start up TigerGraph in a Docker container. |
Video walk-through:
Preparation
Before you can install the TigerGraph system, you need the following:
-
One or more machines that meet the minimum Hardware and Software Requirements
-
A Linux superuser with the same username and login credential on every machine
-
A license key provided by TigerGraph (not applicable to Enterprise Free)
-
A TigerGraph system package
-
If you do not yet have a TigerGraph system package, you can request one.
-
-
If you are installing a cluster, ensure that every machine has the same SSH port and the port stays open during installation
Oracle Linux Server 8
If you install on Oracle Linux Server 8, you need to add authorized users to the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file to enable SSH connections to your machines on these users' accounts.
During TigerGraph installation, you’ll be asked to specify a user to be the TigerGraph Linux user. This user will have access to gadmin commands to manage TigerGraph services. For installation on OEL 8, it’s important to allow SSH connections using the TigerGraph Linux user, along with the Linux user with superuser privileges that you are using to install TigerGraph.
-
For each node, create a Linux OS user with the same username and password. This is the TigerGraph Linux user that you’ll supply during installation.
sudo useradd NEW-USER sudo passwd NEW-USERYou may skip this step, and specify a username during installation to have the installer create the user for you. In that case, you must decide on the username now, and add it to the
sshd_configfile in the next step. -
Add the TigerGraph Linux user as well as any other user you want to allow SSH connections to the AllowUsers row in the
/etc/ssh/sshd_configfile.Make sure all users you want to give access to the SSH server are listed in the AllowUsers row, and ensure that you don’t mistype the usernames. If a user is not listed, no SSH connections are permitted to access their account. Errors could result in you losing remote access to your machine entirely. AllowUsers <tigergrpah_linux_user> <root_user> -
Restart sshd.
/sbin/service sshd restart
This adds firewall rules to allow TCP communication between nodes in the cluster. The installation process will prompt you for these steps. If you have already completed them, ignore and continue.
Installation
TigerGraph’s installation script supports both single-node and cluster installation, and the user can choose to install interactively or non-interactively.
Interactive installation
The following describes the procedure to install TigerGraph on Linux interactively.
Interactive installation allows the user to choose a username and installation file paths besides the defaults.
The filename of your package may vary depending on the product edition and version.
For the examples here, we use the filename tigergraph-<version>.tar.gz, which should be replaced by the actual filename of your package.
Step 1: Extract the package
Extract the package by running the following command to create a folder named tigergraph-<version>-offline.
$ tar -xzf tigergraph-<version>.tar.gzStep 2: Run installation script
Navigate to the tigergraph-<version>-offline folder and run the install.sh script with the following commands:
$ cd tigergraph-<version>-offline
# to install enterprise license
$ sudo ./install.sh
# For non-interactive installations, please see the non-interactive mode section.The installer will ask for the following information. You may choose to hit Enter to skip and use the system default or enter a new value:
-
Your agreement to the License Terms and Conditions
-
Your license key (not applicable for Enterprise Free)
-
Username for the Linux user who will own and manage the TigerGraph platform
-
The installer creates a Linux user with this username who is the only authorized user that can run
gadmincommands to manage the TigerGraph Platform. -
If the installation and data folders are modified from their defaults, the newly created user must have appropriate permissions for these folders. The installation folder requires read/write/execute access, and the other folders require read/write access.
-
-
Password for the Linux user who will own and manage the TigerGraph platform
-
Path to where the installation folder will be
-
Path to where the data folder will be
-
Path to where the log folder will be
-
Path to where the temp folder will be
-
The SSH port for your machine
See the Installation options section below for the default settings.
| License keys are long — over 100 characters long. If you copy-and-paste the license key, be careful not to accidentally include an end-of-line character. |
Step 3: Configure cluster settings
TigerGraph cluster configuration enables the graph database to be partitioned and distributed across multiple server nodes in a local network. After you have answered the questions described in the previous step, the installation script will ask for the following to complete cluster configuration:
-
The number of nodes in your cluster. Each node will be given an alias following the input (
m1,m2,m3, etc.)-
If this is a single-node installation, enter
1
-
-
The IP address of each node
-
Username and credentials information of the sudo user
-
Every machine in the cluster must have a sudo user with the same username and password or SSH key.
-
-
Permission to set NTP time synchronization
-
Permission to set firewall rules among the cluster nodes
| In TigerGraph 3.x, the installation machine can be within or outside the cluster. If outside the cluster, the installation machine still needs to be a Linux machine. |
After all the questions are answered, the script will proceed to installation as shown in this screenshot:
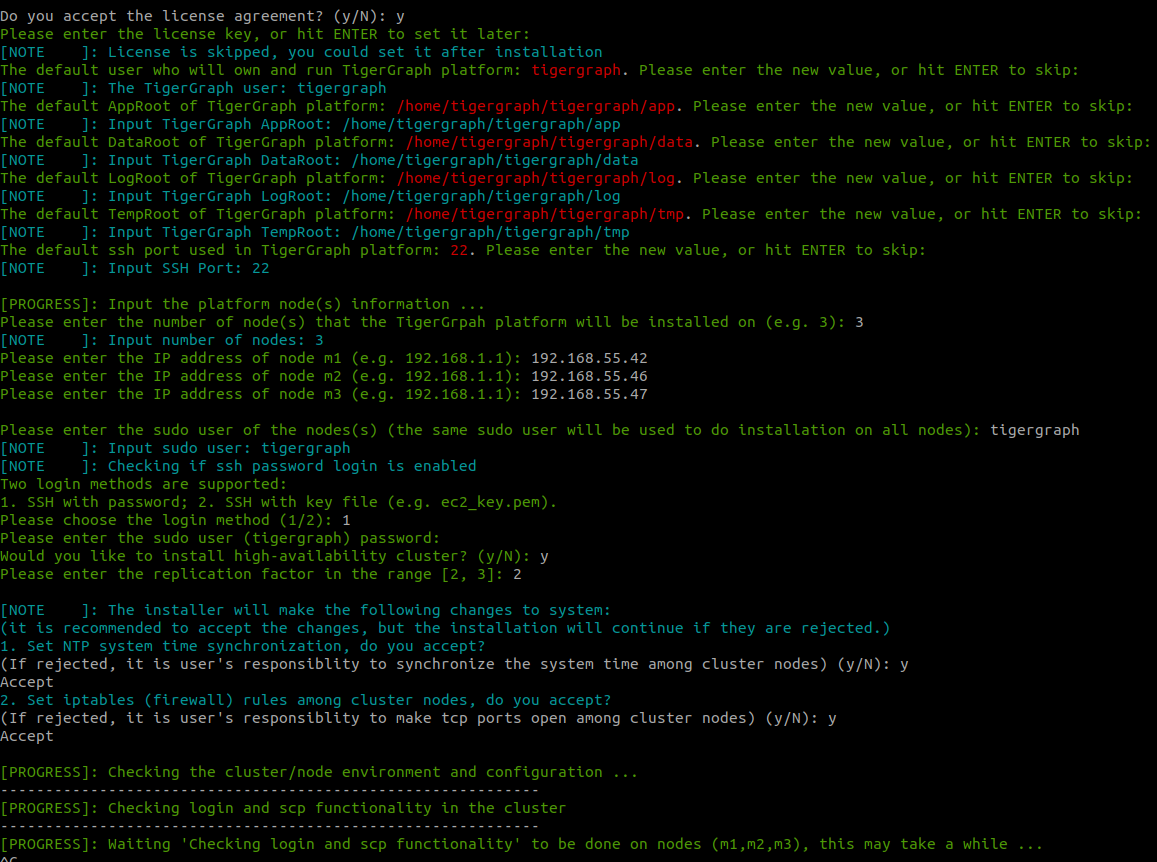
Step 4: Verify installation
After installation is complete, you can switch to the Linux user who owns the platform (created in Step 2) with the following command :
$ su <username> # default username: tigergraphAt the prompt, enter the password that was set in Step 2.
After switching to the correct user, you now have access to gadmin commands. Confirm successful installation by running gadmin status. If the system is installed correctly and the license is activated, the command should report that all services are up and ready. Since there is no graph data loaded yet, GSE and GPE will show "Warmup".
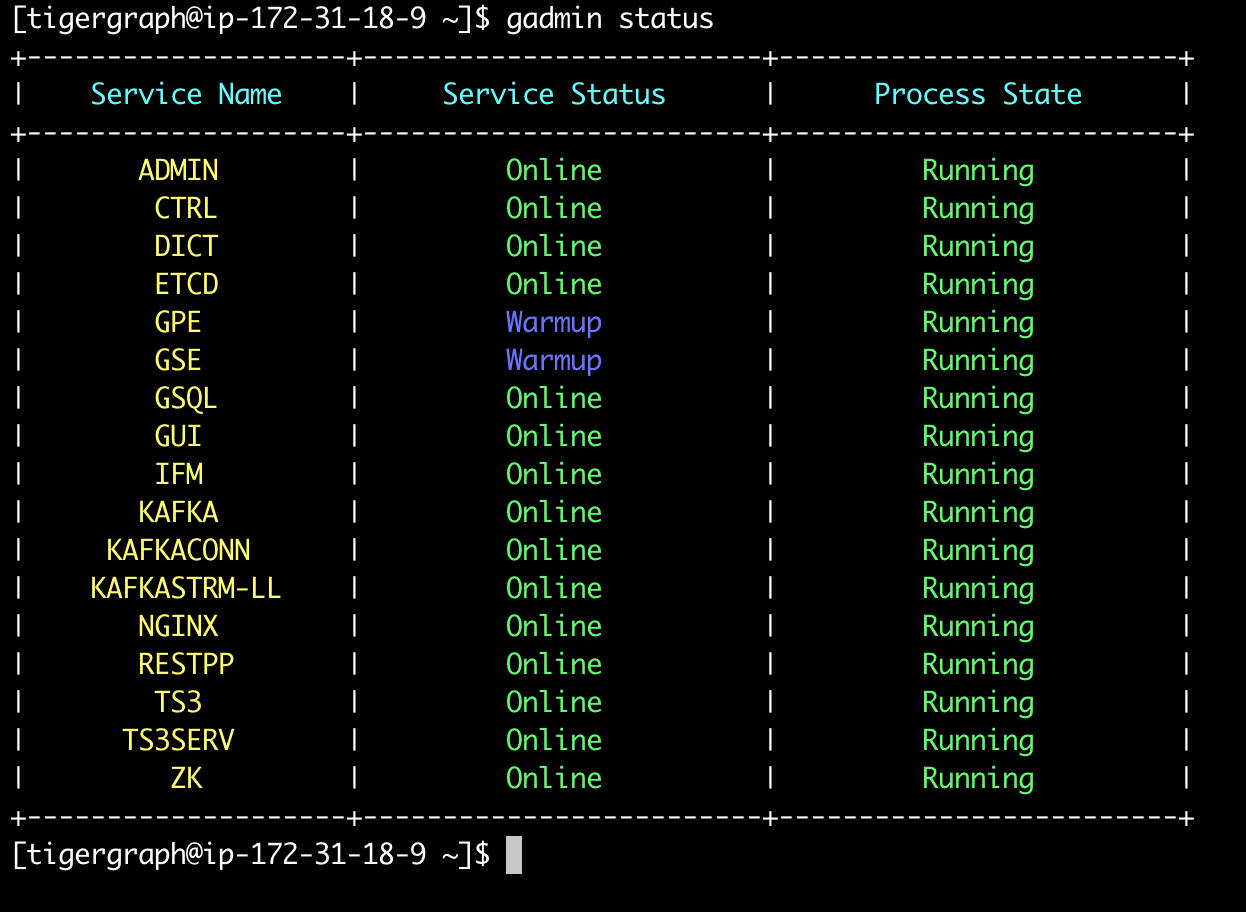
Non-interactive installation
The following describes the procedure to install TigerGraph on Linux non-interactively.
Non-interactive installation uses TigerGraph defaults for all prompts.
Step 1: Extract the package
Extract the package by running the following command to create a folder named tigergraph-<version>-offline.
$ tar -xzf tigergraph-<version>.tar.gzStep 2: Configure installation settings
Navigate to the tigergraph-<version>-offline folder.
Inside the folder, there is a file named install_conf.json.
For non-interactive mode installation, the user must review and modify all the settings in the file install_conf.json before running the installer.
Here is an example install_conf.json file:
{
"BasicConfig": {
"TigerGraph": {
"Username": "tigergraph",
"Password": "secret-password",
"SSHPort": 22,
"PrivateKeyFile": "",
"PublicKeyFile": ""
},
"RootDir": {
"AppRoot": "/home/tigergraph/tigergraph/app",
"DataRoot": "/home/tigergraph/tigergraph/data",
"LogRoot": "/home/tigergraph/tigergraph/log",
"TempRoot": "/home/tigergraph/tigergraph/tmp"
},
"License": "eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJJc3N1ZXIiOiJUaWdlckdyYXBoIEluYy4iLCJBdWRpZW5jZSI6IlRpZ2VyR3JhcGggRnJlZSIsIlN0YXJ0VGltZSI6MTYxNzM1NTgwMywiRW5kVGltZSI6MTY1MTQ4NzQwMywiSXNzdWVUaW1lIjoxNjE3MzU5NDAzLCJFZGl0aW9uIjoiRW50ZXJwcmlzZSIsIlZlcnNpb24iOiJBbGwiLCJIb3N0Ijp7Ik1heENQVUNvcmUiOjEwMDAwMDAwMDAwMDAwMDAsIk1heFBoeXNpY2FsTWVtb3J5Qnl0ZXMiOjEwMDAwMDAwMDAwMDAwMDAsIk1heENsdXN0ZXJOb2RlTnVtYmVyIjoxMDI0fSwiVG9wb2xvZ3kiOnsiTWF4VmVydGV4TnVtYmVyIjoxMDAwMDAwMDAwMDAwMDAwLCJNYXhFZGdlTnVtYmVyIjoxMDAwMDAwMDAwMDAwMDAwLCJNYXhHcmFwaE51bWJlciI6MTAyNCwiTWF4VG9wb2xvZ3lCeXRlcyI6NTM2ODcwNjM3MTJ9LCJHU1QiOnsiRW5hYmxlIjp0cnVlLCJab29tQ2hhcnRzTGljZW5zZSI6IntcbiAgXCJsaWNlbnNlXCI6IFwiWkNCLTRtZmk3NDRsdjogWm9vbUNoYXJ0cyBFbnRlcnByaXNlIGxpY2VuY2UgZm9yIFRpZ2VyR3JhcGggZm9yIG9mZmxpbmUgdXNlOyB1cGdyYWRlcyB1bnRpbDogMjAyMi0xMi0zMVwiLFxuICBcImxpY2Vuc2VLZXlcIjogXCI4Zjg2ZWQzM2Y0ZWJmYmE4YTI4NjlkZGUzMmYzYTMwZGI4NGEzOTgxYmEzNmZhZWZlYTMxNDhhYzY4MzkxZTlhYzUzZDU3YmI5MjdmNjY5YWI1ZWJhYzJhYmQ3YTFkNDBiM2UxNDRmZjIwMDYyZWNiZmIwZjJiN2I0ZWFmZWIwYzU2NTc2NjBhZGExZDc1MWNhODU3NWZhYTE1ZWQwODI0NzkwZWQxMjJkY2Q4NjcyZTJiN2QzN2MwNmE3MzFhYTc2MDIwM2FhYmMwYjYzOWEzMjBhOGQxNmI0YmFiNGY5NTJiNTMwOTUzMWI4MDkxNjYwZDVjOGMzNGY0NmMyNjZiOGZiNzc2YzFmN2Y0MTdlMGQ5Y2JkZGFlOTExNTFlY2Y3YmMzZDlkNDgyNWE2MjAwYzk0MWMyMDE4ZDY4YjkyOWE5ZWY2MzQ2MDE5NjFhYmU1MGI0ZTk0ZmY5Y2VjMjA1ODEwYmVlZmRkM2NlZDU2YjM5NTVjYmE0YWIyMGNiNzc5MWE0NmQxNzIwMzNiZmI0ZDIyMDM4ODZhZTllZDFkOWMzOWIyOTM2ODc3Yjc2NzY4ZjQwNWQ5Y2MwY2JlODVjOTE2NDllMDI5YTA0NDFlOGFmYjA2MzY4MTMxZGM1YTc1NDEyOTc1NjFlMDRlMGM1MzE1ZmFjMDdhYzViOWViM1wiXG59In0sIlJ1bnRpbWVNZW1vcnkiOnsiTWF4VXNlclJlc2lkZW50U2V0Qnl0ZXMiOjEwMDAwMDAwMDAwMDAwMDB9fQ.B1tR-ZyzFB3WCtCXBl-CXb-3YlL1Hy1btCzsEnkLd6GE2AOvJdpqVZGU-YGyIaOGSYX1sbjrePBoupuWPwrOgvce-mq_Qwp8eounoEOkuzYlTQXFj3lM1wO6vrdiOn2GUm0qMVtlVTIDrFZlZ-bWcdSUA4J8t2JNJrYxQgPWjlO9f4I4w2RbTK3sZW7N96bqFUQPituiwLcPX_VSVT8KBluM2WIH7CJitHl21IbnQbwScBw_QgjfaITZXE6UXisMM9XNphf5yQX9arFDQLchV7e2i3R2tUEuF7V_mHFrVa8vCBjm_0uABzcY8U02QJ78SB9MgLNrqgtzIwHmYP22KQ",
"NodeList": [
"m1: 127.0.0.1"
]
},
"AdvancedConfig": {
"ClusterConfig": {
"LoginConfig": {
"SudoUser": "sudoUserName",
"Method": "P[or K]",
"P": "<sudo_user_password>",
"K": "</path/to/my_key.pem_rsa>"
},
"ReplicationFactor": 1
}
}
}Here is a description of all the fields in the config file:
-
"BasicConfig"-
"TigerGraph": Information about the Linux user that will be created by the installer who owns and manages the TigerGraph platform.-
"Username": Username of the Linux user. -
"Password": Password of the Linux user. -
"SSHPort": Port number used to establish SSH connections. -
"PrivateKeyFile"(optional): Absolute path to a valid private key file. If left empty, TigerGraph will generate one namedtigergraph.rsaautomatically. -
"PublicKeyFile"(optional): Absolute path to a valid public key file. If left empty, TigerGraph will generate one namedtigergraph.pubautomatically.
-
-
"RootDir"-
"AppRoot": Absolute path to where application folder will be. -
"DataRoot": Absolute path to where the data folder will be. -
"LogRoot": Absolute path to where the log folder will be. -
"TempRoot": Absolute path to where the temp folder will be.
-
-
"License": Your TigerGraph license string. -
"Node List": A JSON array of the nodes in the cluster. Each machine in the cluster is defined as a key-value pair, where the key is a machine alias (m1, m2, m3, etc.) and the value is the IP address of the node.
-
-
"AdvancedConfig"-
"ClusterConfig": Cluster configurations-
"LoginConfig": Login configurations-
"SudoUser": Username of the sudo user who will be used to execute the installation on all nodes. -
"Method": Authentication method for SSH. Enter"P"to use password authentication and"K"to use key-based authentication. If you use key-based authentication, the sudo user you are providing must have password-less sudo access on all nodes in the cluster. -
"P": Password of the sudo user. -
"K": Absolute path to the SSH key to be used to authenticate the sudo user.
-
-
"ReplicationFactor": Replication factor of the cluster.-
If you would like to enable the High Availability (HA) feature, please make sure you have at least 3 nodes in the cluster and set the replication factor to be greater than 1. For example, if your cluster has 6 nodes, you could set the replication factor to be 2 or 3. If you set the replication factor to be 2, then the partitioning factor will be 6 / 2 = 3. Therefore, 3 nodes will be used for one copy of the data, and the other 3 nodes will be used as a replica copy of the data.
-
Ensure that the total number of nodes can be fully divided by the replication factor. Otherwise, some nodes may not be utilized as parts of the HA cluster.
-
-
-
| Deploying a database without changing the default password for the TigerGraph superuser is a security risk. |
If you alter the RootDir folder paths, make sure the new user created to manage the platform has the appropriate permissions.
The user needs read/write/execute permissions on AppRoot and read/write permissions on the other folders at a minimum.
|
Installation options
The following default settings will be applied if no parameters are specified:
-
The installer will create a Linux user with username
tigergraphand with passwordtigergraph.This user will be the only user authorized to rungadmincommands to manage the TigerGraph platform and services.-
If there is already a user named
tigergraph, this user will be designated as the platform owner and no other user will be created.
-
-
The default root directory for the installation would be
/home/tigergraph/tigergraphwith the App/Data/Log/Temp files within it :-
App Path :
/home/tigergraph/tigergraph/app -
Data Path :
/home/tigergraph/tigergraph/data -
Log Path :
/home/tigergraph/tigergraph/log -
Temp Path :
/home/tigergraph/tigergraph/tmp
-
-
The root directory for the installation (referred to as
<tigerGraph_root_dir>) is a folder calledtigergraphlocated in the TigerGraph Linux user’s home directory. For example,/home/tigergraph/tigergraph.
The installation can be customized by running command-line options with the install.sh script:
Command-line options
# Command-line options for install.sh
Usage:
./install.sh [-n] [-u <user>] [-p <password>] [-r <tigergraph_root_dir>] [-l <license_key>] [-F] [-N]
./install.sh -h
Options:
-h -- Show help information
-u -- Username of Linux user to create [default: tigergraph]
-p -- Password of Linux user to create [default: tigergraph]
-l -- TigerGraph license key
-n -- Non-interactive option: suppress prompts, and install
using default config
-F -- Set iptables (firewall) rules to open TCP ports among cluster nodes
-N -- Set NTP system time synchronization among cluster nodes
[NOTE ]: Using option '-n' will non-interactively install the platform
on single node or cluster with all configurations from
config file "install_config.json". In this case, the config
file should be modified before installation.
[WARNING ]: Installer will fail if any option (except -F and -N)
is provided with option '-n' at the same time.