High Availability Support for GSQL Server
TigerGraph has built-in HA for all the internal critical components. That is, if one component becomes unavailable, then a corresponding component located within another cluster node can take over. Due to the criticality of the interworking of these internal components, users are advised not to alter the number of such internal nodes except as advised by Tigergraph Support or Professional Services.
When a cluster is initially installed or resized, the installer will automatically select an appropriate number of service components. For components which comprise the core storage and compute engine (such GSE, GPE, and REST API servers), one service component per cluster node is appropriate. For other components, like the GSQL server, having one component per node is excessive for large clusters. The maximum number of GSQL servers is 5, regardless of cluster size.
Design overview
The first five nodes in a TigerGraph cluster each run a GSQL server. One of the GSQL servers is the primary server, while other servers are standby servers that provide high availability for client connections. The primary and standby servers are referred to as "leaders" and "followers" inside GSQL.
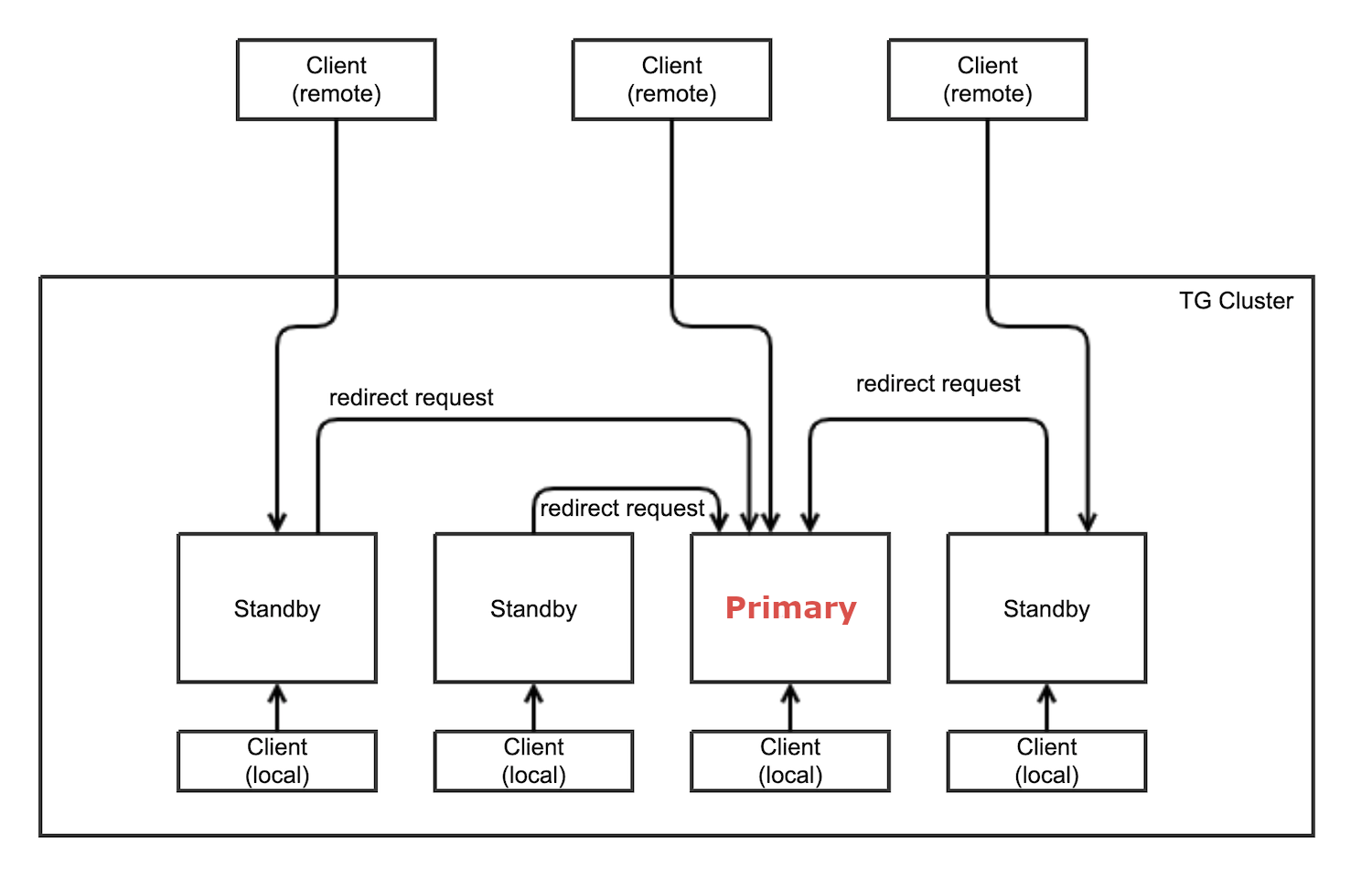
Role of primary GSQL server
The primary GSQL server performs the following tasks:
-
Processes client connections
-
Processes query requests from GSQL clients
-
Processes user management requests
When the primary server fails, a standby server becomes the new primary server. When the old primary server is restored, it becomes a GSQL standby server.
Configuring HA for the GSQL server
Setting GSQL HA Failover
Use the gadmin config command to get/set the following configurations related to GSQL High Availability.
The first is the heartbeat interval in milliseconds. The second is the number of consecutively missed heartbeats that will trigger switching to a backup server. It must be at least 2 to allow 1 heartbeat miss.
Controller.LeaderElectionHeartBeatIntervalMS = 2000
Controller.LeaderElectionHeartBeatMaxMiss = 4For example, if we use LeaderElectionHeartBeatIntervalMS = 2000 and LeaderElectionHeartBeatMaxMiss = 4 as shown above, then the total timeout is 2 × 4 = 8 seconds.
In this case, the current primary server will be switched if its heartbeat has stopped for more than 8 seconds.
User Impact and Changes
UDF and token function retrieval
The m1 node of a cluster stores the following files that may contain user-defined C++ functions to customize GSQL:
-
GSQL loader’s Token functions
-
ExprFunctions
-
ExprUtil
The GSQL server will retrieve these user source code files in the following priority order when it needs them:
-
Via GitHub/GitHub enterprise (if configuration is set),
-
Files uploaded via
PUTcommands -
Default files that are shipped with the product
User source code in GitHub code repository
This mode requires public network access or GitHub enterprise server access.
Provide the following gadmin configuration:
GSQL.GithubUserAcessToken # the credential, or "anonymous", empty means not using github
GSQL.GithubRepository # e.g. tigergraph/ecosys
GSQL.GithubBranch # optional; default is "main" branch, e.g. demo_github
GSQL.GithubPath # path to the directory in the github that has TokenBank.cpp, ExprFunctions.hpp, ExprUtil.hpp, e.g. sample_code/src
GSQL.GithubUrl # optional, used for github enterprise, e.g. https://api.github.comExample:
gadmin config set GSQL.GithubUserAcessToken anonymous
gadmin config set GSQL.GithubRepository tigergraph/ecosys
gadmin config set GSQL.GithubBranch demo_github
gadmin config set GSQL.GithubPath sample_code/src
gadmin config applyWhen the GSQL server needs to compile the files, it will retrieve them from GitHub if the GitHub access is configured as above.
It will retry 3 times, with a five-second timeout each time.
If the connection fails, it will go to the next priority level method, i.e. file uploaded via PUT commands.
Upload source code
PUT TokenBank FROM "path/to/a/file"
PUT ExprFunctions FROM "path/to/a/file"
PUT ExprUtil FROM "path/to/a/file"Example:
temp_TokenBank=$tempDir/tmp_TokenBank.cpp
temp_ExprFunctions=$tempDir/tmp_ExprFunctions.hpp
temp_ExprUtil=$tempDir/tmp_ExprUtil.hpp
eval gsql 'PUT TokenBank FROM \"$temp_TokenBank\"'
eval gsql 'PUT ExprFunctions FROM \"$temp_ExprFunctions\"'
eval gsql 'PUT ExprUtil FROM \"$temp_ExprUtil\"'Download source code
GET TokenBank TO "path/to/a/file"
GET ExprFunctions TO "path/to/a/file"
GET ExprUtil TO "path/to/a/file"Example:
temp_TokenBank2=$tempDir/tmp_TokenBank_2.cpp
temp_ExprFunctions2=$tempDir/tmp_ExprFunctions_2.hpp
temp_ExprUtil2=$tempDir/tmp_ExprUtil_2.hpp
echo "GET TokenBank.cpp, ExprFunctions.hpp and ExprUtil.hpp to current node."
eval gsql 'GET TokenBank TO \"$temp_TokenBank2\"'
eval gsql 'GET ExprFunctions TO \"$temp_ExprFunctions2\"'
eval gsql 'GET ExprUtil TO \"$temp_ExprUtil2\"'The uploaded files will be saved to all nodes. Users need to have the READ_FILE privilege to run GET and the WRITE_FILE privilege to run PUT.
With the GET command, the user can download the corresponding file from the primary node to a local directory at the current cluster node.
With the PUT command, the local file will be copied to all cluster nodes, including itself.
Example usage scenario to update the files:
// Download the current file via GET, or create a new file from draft;
GET TokenBank TO "/myFolder/file.cpp"
// Upload the file via PUT
PUT TokenBank FROM "/myFolder/file.cpp"For each cluster node, TokenBank.cpp is stored at:
$(gadmin config get System.DataRoot)/gsql/tokenbank/ExprFunctions.hpp and ExprUtil.hpp files are stored at:
$(gadmin config get System.DataRoot)/gsql/udf/The full path should be provided including the file name for PUT/GET, eg:
put ExprFunctions from "/home/path/tmp/ExprFunc.hpp"
get TokenBank to "doc/path/tmp/myTB.cpp"In the first command, we used the absolute path, while in the second command, we used the relative path.
Both are supported, however, ~ is not supported (such as in ~/tmp/x.hpp).
If you use a folder name, the default file name will be used.
put ExprFunctions from "/home/path/tmp"This will use an ExprFunctions.hpp file under the server directory "/home/path/tmp" for PUT.
get TokenBank to "home/path/tmp/"This will create/overwrite the file "home/path/tmp/TokenBank.cpp".
If the file name is given in the path, its file extension must match the file type expected.
put ExprFunctions from "/home/path/tmp/test1.gsql"This is not allowed, since PUT/GET ExprFunctions must use .hpp as the file extension.
Default file shipped with TigerGraph package
If the corresponding file is not found, the GSQL Primary server will use the default file in the package. These default files are at:
$(gadmin config get System.AppRoot)/dev/gdk/gsql/src/TokenBank/TokenBank.cpp
$(gadmin config get System.AppRoot)/dev/gdk/gsql/src/QueryUdf/ExprUtil.hpp
$(gadmin config get System.AppRoot)/dev/gdk/gsql/src/QueryUdf/ExprFunctions.hppFile Path Configuration
Before TigerGraph version 3.1, the file path used in loading jobs referred to the file in m1, unless the user specified the machine name before the path (ALL, ANY, m1, m2,…).
Now, the primary server can be running on any machine, and can be switched.
This means the GSQL server may or may not find the file. To be backwards-compatible with previous versions of TigerGraph, prefix a machine name if the client is in the TigerGraph cluster.
Users can specify the node ID before the path using ALL, ANY, m1, m2 and so on.
Declaring ALL or ANY as host ID will load files from every cluster node.
Use the syntax m1|m3|m4 to declare the combination of several nodes.
If the hosts are not specified, it will look for the host ID of the current node that is running the loading job, (through searching the nodes in $(gadmin config get GSQL.BasicConfig.Nodes)). If not found, it will use node m1 by default.
# current refers to /path/to/csv in m1
LOAD "/path/to/csv" TO VERTEX vt VALUES($0)
LOAD "ALL:/path/to/csv" TO VERTEX vt VALUES($0)
LOAD "m1|m2:/path/to/csv" TO VERTEX vt VALUES($0)A data source can be created and used with a file path or a JSON string.
create data_source kafka k1 for graph poc_graph
set k1 = "/tmp/kafka_config.json"
create data_source kafka k2 = "/tmp/kafka_config.json"
CREATE LOADING JOB load_kafka FOR GRAPH poc_graph {
DEFINE FILENAME f1 = "$k1:/tmp/topic_partition_config.json";
LOAD f1
TO VERTEX MyNode VALUES ($2)
USING SEPARATOR="|";
}GSQL Client connection setup
The GSQL client can connect to the GSQL server in one of several ways according to the following priority order:
Using IP address
Users can specify the IP address and port when calling the GSQL client using gsql -i or gsql -ip. For example:
gsql -ip 192.168.11.32:14240,192.168.11.34:14240,192.168.11.36The GSQL clients will try these IPs and ports one by one. The port is optional. Port 14240, the default port for the GSQL server, will be used if no port is specified.
Using GSQL IP Configuration
If gsql -i or gsql -ip are not used, the GSQL client will search the file gsql_server_ip_config where the user runs the GSQL client. The file gsql_server_ip_config should be a one-line file such as shown below. GSQL client will traverse the ips and ports in the file in its order.
172.18.0.101,172.18.0.102:14240,172.18.0.103:14240The port number is also optional here, using 14240 by default.